|
In the previous page,
we just got started with the walkthrough. Let's continue
with Step 3 on this page.
With both the left loop and right loop terminated at the
unordered values, we need to perform the swap. The swap code
is the pink section of code:

Before we
swap, we need to make sure that the left value is truly to
the left of our right value. In other words, i <= j. This
makes sure that we don't perform a reverse swap. Without
this check, our code would simply run forever also.
The value of i (0) is still less than the value of
j (2). And so the
swap begins. The array value referenced by i, 4, is stored in a temporary
value:
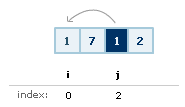
You then set the array value at i to
equal the array value at j:
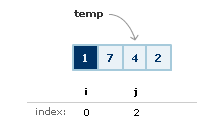
After the value at i is set, you set the temporary value, the value at
i
you determined a few steps ago, to the value at j:
As a quick observation, notice that your pivot point is
still referencing the array value
1 and not the index position of
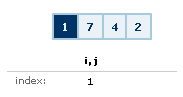
the array value. Finally, you increase the value of
i and decrease the value of j.
This is done to make sure you are not analyzing the same
values again:
We are about half-way through this article, so feel free
stretch for a bit or take a break. There is more on the
next page!
|