by
Brian Haveri aka bwh2 |
2 October 2006
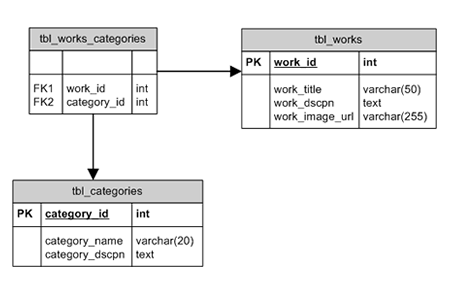
If each table only has one job, then the job for
tbl_works_categories will be to link specific works to
specific categories. Thus, it will only hold two
columns: work_id and category_id. Both columns are
called Foreign Keys. Columns designated as foreign keys
will hold values that are primary keys in other tables.
That is, work_id is a primary key in tbl_works. In
tbl_works_categories, the column work_id is a foreign
key. The same goes for category_id and tbl_categories.
/***** CREATE tbl_works_categories *****/
CREATE TABLE `tbl_works_categories` (
`work_id` INT NOT NULL,
`category_id` INT NOT NULL
)
TYPE = myisam;
/***** End CREATE *****/
/***** INSERT sample data into
tbl_works_categories *****/
INSERT INTO `tbl_works_categories` (
`work_id`,
`category_id`
)
VALUES (
'1',
'1'
);
INSERT INTO `tbl_works_categories` (
`work_id`,
`category_id`
)
VALUES (
'2',
'1'
);
INSERT INTO `tbl_works_categories` (
`work_id`,
`category_id`
)
VALUES (
'3',
'2'
);
INSERT INTO `tbl_works_categories` (
`work_id`,
`category_id`
)
VALUES (
'4',
'1'
);
/***** End INSERT *****/
Note that we use work_id and category_id
because these ID numbers are unique to each row in
tbl_works and tbl_categories, respectively. If we had
instead used category_name and work_title in
tbl_works_categories, we would have redundant data -
data that is duplicated elsewhere. Unlike name fields
such as category_name, ID fields are never subject to
change, so using them to identify a row is safer and
requires less storage and rework. The process of
removing redundant data is called Database
Normalization. The structure for tbl_works_categories is
shown in the following ERD as well as the relationships
to tbl_works and tbl_categories.
Onwards to the
next page!
|