# Closures in JavaScript
by [kirupa](https://www.kirupa.com/me/index.htm) | filed under [JavaScript 101](https://www.kirupa.com/javascript/learn_javascript.htm)
By now, you probably know all about [ functions](https://www.kirupa.com/html5/functions_in_javascript.htm) and all the fun functiony things that they do. An important part of working with functions, with JavaScript, and (possibly) life in general is understanding the topic known as **closures**. Closures touch upon a gray area where functions and [variable scope](https://www.kirupa.com/html5/variable_scope_js.htm) intersect:
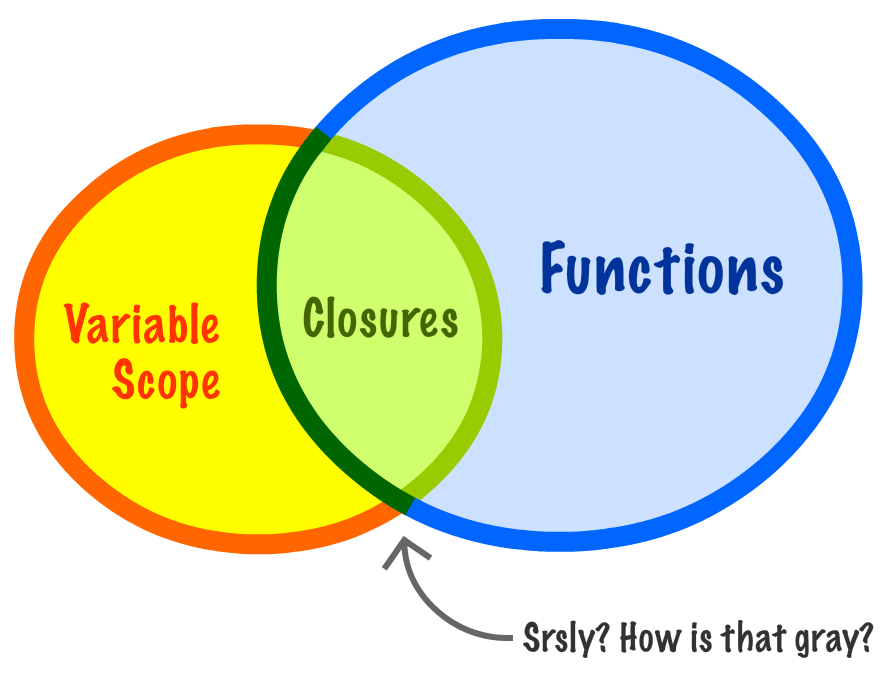
Now, I am not going to say any more about closures, for this is something best explained by seeing code. Any words I add right now to define or describe what closures are will only serve to confuse things. In the following sections, we'll start off in familiar territory and then slowly venture into hostile areas where closures can be found.
Onwards!
## Functions within Functions
The first thing we are going to do is really drill in on what happens when you have functions within functions...and the inner function gets returned. As part of that, let's do a quick review of functions.
Take a look at the following code:
```js
function calculateRectangleArea(length, width) {
return length * width;
}
var roomArea = calculateRectangleArea(10, 10);
alert(roomArea);
```
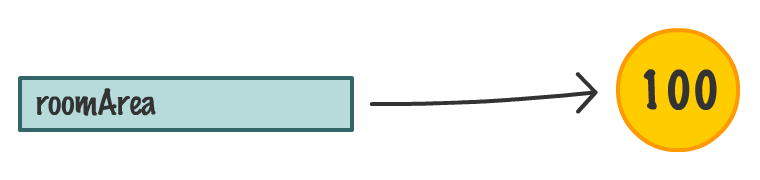
The `calculateRectangleArea` function takes two arguments and returns the multiplied value of those arguments to whatever called it. In this example, the ***whatever called it part*** is played by the `roomArea` variable.
After this code has run, the `roomArea` variable contains the result of multiplying 10 and 10...which is simply 100:
As you know, what a function returns can pretty much be anything. In this case, we returned a number. You can very easily return some text (aka a [ String](https://www.kirupa.com/html5/strings_in_javascript.htm)), the `undefined` value, a [ custom object,](https://www.kirupa.com/html5/a_deeper_look_at_objects_in_javascript.htm) etc. As long as the code that is calling the function knows what to do with what the function returns, you can do pretty much whatever you want. You can even return another function. Let me rathole on this a bit.
Below is a very simple example of what I am talking about:
```js
function youSayGoodBye() {
alert("Good Bye!");
function andISayHello() {
alert("Hello!");
}
return andISayHello;
}
```
We can have functions that contain functions inside them. In this example, we have our `youSayGoodBye` function that contains an `alert` and another function called `andISayHello`:

The interesting part is what the ` youSayGoodBye` function returns when it gets called. It returns the `andISayHello` function:
```js
function youSayGoodBye() {
alert("Good Bye!");
function andISayHello() {
alert("Hello!");
}
return andISayHello;
}
```
Let's go ahead and play this example out. To call this function, initialize a variable that points to ` youSayGoodBye`:
```js
var something = youSayGoodBye();
```
The moment this line of code runs, **all of the code** inside your `youSayGoodBye` function will get run as well. This means, you will see a dialog (thanks to the `alert`) that says **Good Bye!**:

As part of running to completion, the ` andISayHello` function will be created and then returned as well. At this point, our `something` variable only has eyes for one thing, and that thing is the ` andISayHello` function:

The `youSayGoodBye` outer function, from the `something` variable's point of view, simply goes away. Because the `something` variable now points to a function, you can invoke this function by just calling it using the open and close parentheses like you normally would:
```js
var something = youSayGoodBye();
something();
```
When you do this, the returned inner function (aka `andISayHello`) will execute. Just like before, you will see a dialog appear, but this dialog will say **Hello**! - which is what the `alert` inside this function specified:

All of this should probably a review. The only thing that you may have found new is realizing once a function returns a value, it is no longer around. The only thing that remains is the returned value.
Ok, we are getting close to the promised hostile territory. In the next section, we will extend what we've just seen by taking a look at another example with a slight twist.
## When the Inner Functions Aren't Self-Contained
In the previous example, our `andISayHello` inner function was self-contained and didn't rely on any variables or state from the outer function:
```js
function youSayGoodBye() {
alert("Good Bye!");
function andISayHello() {
alert("Hello!");
}
return andISayHello;
}
```
In many real scenarios, very rarely will we run into a case like this. We will often have variables and data that are shared between the outer function and the inner function. To highlight this, take a look at the following:
```js
function stopWatch() {
var startTime = Date.now();
function getDelay() {
var elapsedTime = Date.now() - startTime;
alert(elapsedTime);
}
return getDelay;
}
```
This example shows a very simple way of measuring the time it takes to do something. Inside the `stopWatch` function, we have a `startTime` variable that is set to the value of `Date.now()`:
```js
function stopWatch() {
var startTime = Date.now();
function getDelay() {
var elapsedTime = Date.now() - startTime;
alert(elapsedTime);
}
return getDelay;
}
```
We also have an inner function called ` getDelay`:
```js
function stopWatch() {
var startTime = Date.now();
function getDelay() {
var elapsedTime = Date.now() - startTime;
alert(elapsedTime);
}
return getDelay;
}
```
The `getDelay` function displays a dialog containing the difference in time between a new call to `Date.now()` and the `startTime` variable declared earlier.
Getting back to the outer `stopWatch` function, the last thing that happens is that it returns the `getDelay` function before exiting. As we can see, the code here is very similar to the earlier example. We have an outer function, we have an inner function, and we have the outer function returning the inner function.
Now, to see the `stopWatch` function at work, add the following lines of code:
```js
var timer = stopWatch();
// do something that takes some time
for (var i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
var foo = Math.random() * 10000;
}
// invoke the returned function
timer();
```
The full markup and code for this example looks as follows:
```js
Closures
```
If you run this example, we'll see a dialog displaying the number of milliseconds it took between your `timer` variable getting initialized, your `for` loop running to completion, and the `timer` variable getting invoked as a function:

To explain in a different way, we have a stopwatch that we invoke, run some long-running operation, and invoke again to see how long the long-running operation took place.
Now that we can see our little stopwatch example working, let's go back to the `stopWatch` function and see what exactly is going on. Like I mentioned a few lines ago, a lot of what we see is similar to the `youSayGoodBye` / `andISayHello` example. There is a twist that makes this example different, and the important part to note is what happens when the `getDelay` function is returned to the `timer` variable.
Here is an incomplete visualization of what this looks like:
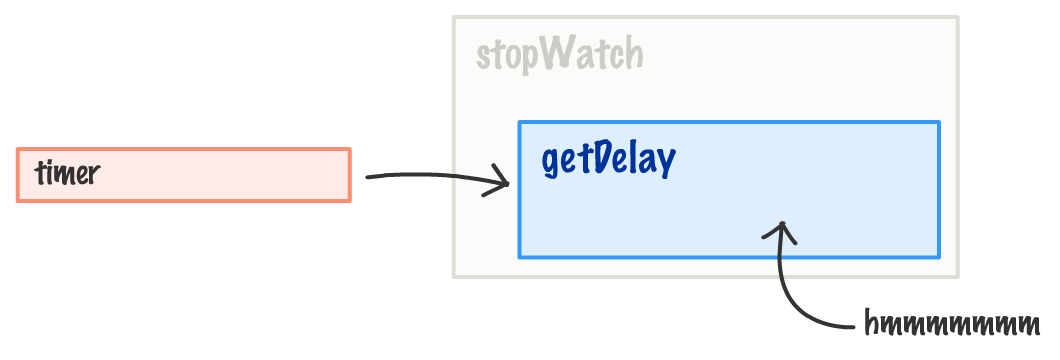
The `stopWatch` outer function is no longer in play, and the `timer` variable is bound to the `getDelay` function. Now, here is the twist. The `getDelay` function relies on the `startTime` variable that lives in the context of the outer ` stopWatch` function:
```js
function stopWatch() {
var startTime = Date.now();
function getDelay() {
var elapsedTime = Date.now() - startTime;
alert(elapsedTime);
}
return getDelay;
}
```
When the outer `stopWatch` function goes away when `getDelay` is returned to the `timer` variable, what happens in the following line?
```js
function getDelay() {
var elapsedTime = Date.now() - startTime;
alert(elapsedTime);
}
```
In this context, it would make sense if the `startTime` variable is actually undefined, right? But, the example totally worked, so something else is going on here. That something else is the shy and mysterious closure. Here is a look at what happens to make our `startTime` variable actually store a value and not be undefined.
The JavaScript runtime that keeps track of all of your variables, memory usage, references, and so on is really clever. In this example, it detects that the inner function (`getDelay`) is relying on variables from the outer function (`stopWatch`). When that happens, the runtime ensures that any variables in the outer function that are needed are still available to the inner function **even if the outer function goes away**.
To visualize this properly, here is what the ` timer` variable looks like:
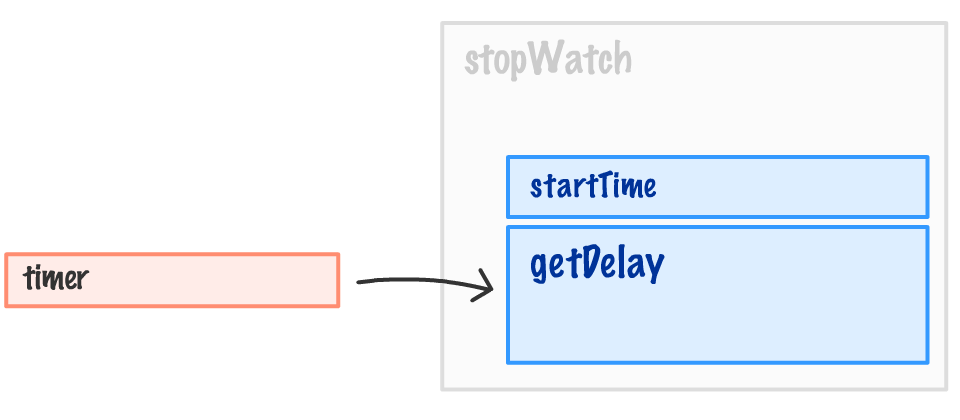
It is still referring to the `getDelay` function, but the `getDelay` function also has access to the `startTime` variable that existed in the outer `stopWatch` function. This inner function, because it **enclosed** relevant variables from the outer function into its bubble (aka scope), is known as a **closure**:
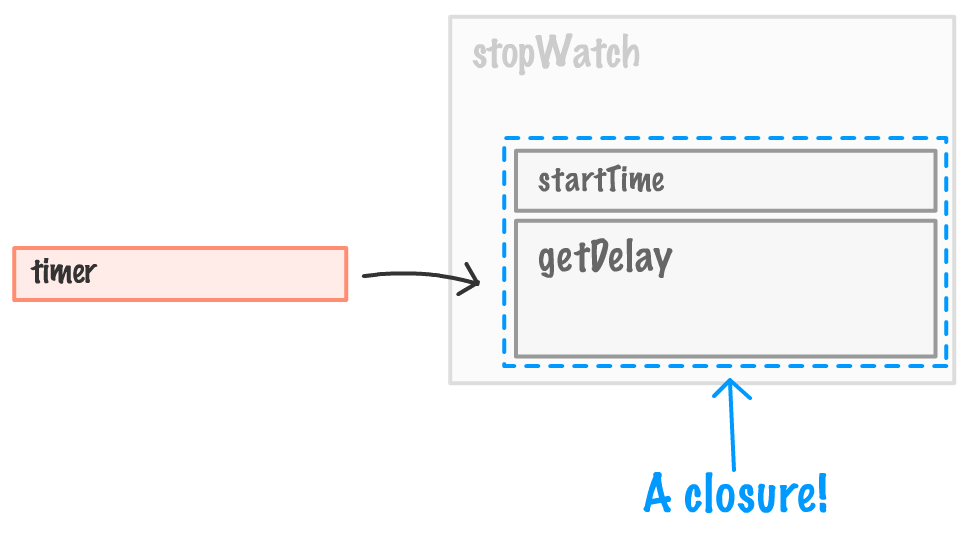
To define the closure more formally, it is a **newly created function that also contains its variable context**:
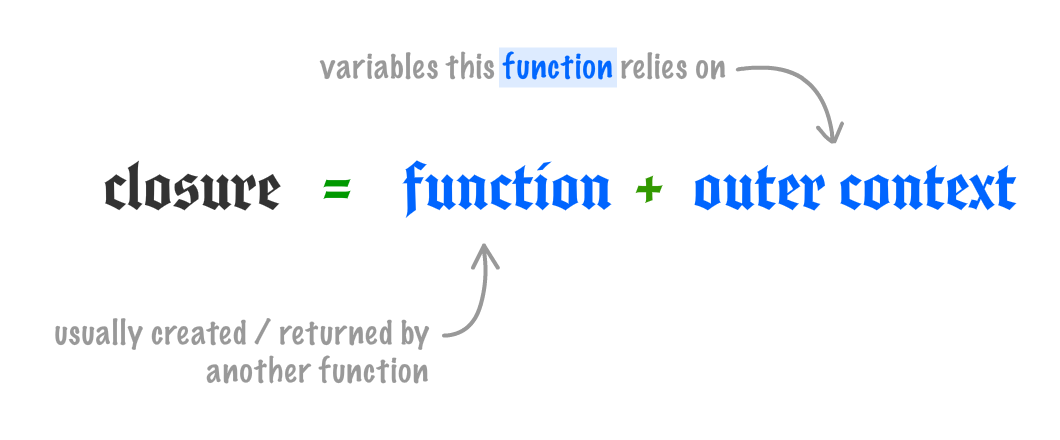
To review this one more time using our existing example, the `startTime` variable gets the value of `Date.now` the moment the `timer` variable gets initialized and the `stopWatch` function runs. When the `stopWatch` function returns the inner `getDelay` function, the `stopWatch` function goes away. What doesn't go away are any shared variables inside ` stopWatch` that the inner function relies on. Those shared variables are not destroyed. Instead, they are enclosed by the inner function aka the closure.
## Wrapping up Closures
By looking at closures through examples first, we really missed out on a lot of boring definitions, theories, and hand waving. In all seriousness, closures are very common in JavaScript. We will encounter them in many subtle and not-so-subtle ways:

If there is only thing you take out of all of this, remember the following: **The most important thing closures do is allow functions to keep on working even if their environment drastically changes or disappears.** Any variables that were in scope when the function was created are enclosed and protected to ensure the function still works. This behavior is essential for a very dynamic language like JavaScript where you often create, modify, and destroy things on the fly.